CPP tutorials
C++ Keywords

Keywords are the reserved words that have special meanings. Since their meanings are reserved, we cannot redefine them or use them for a different purpose.
C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// 'int' is a keyword
int main() {
// 'int' is a keyword
int age = 20;
// 'if' is a keyword
if (age > 18) {
cout << "Adult";
}
// 'return' is a keyword
return 0;
}
Output
Adult
How to Identify C++ Keywords
- Syntax Highlighting: Most modern IDEs (like Visual Studio, CLion, Code::Blocks) highlight keywords in a different color. This makes them stand out from variables or function names.
- Compiler Errors: If you mistakenly use a keyword as a variable name, your code won’t compile. Example:
C++
int return = 10; // Error: 'return' is reserved
Categorization of C++ Keywords
To make them easier to understand, let’s group C++ keywords by context:
| Category | Keywords |
|---|---|
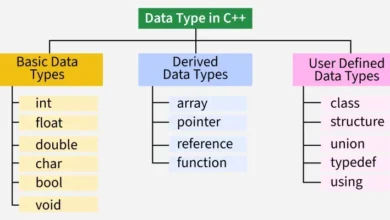
| Data Types | bool, char, char8_t, char16_t, char32_t, int, long, short, signed, unsigned, float, double, void, wchar_t |
| Control Flow | if, else, switch, case, default, for, while, do, break, continue, goto |
| Boolean & Null | true, false, nullptr |
| Memory Management | new, delete, sizeof, alignas, alignof |
| Classes & Structs | class, struct, union, enum, friend, mutable, this |
| Access Specifiers | public, private, protected |
| Functions & Modifiers | inline, explicit, virtual, override, final, constexpr, consteval, constinit, operator, typedef, using, typename |
| Templates & Generics | template, concept, requires |
| Exception Handling | try, catch, throw, noexcept |
| Casting & Type Info | const_cast, dynamic_cast, reinterpret_cast, static_cast, decltype, typeid |
| Constants & Storage | const, static, static_assert, extern, register, thread_local, volatile |
| Modules / Export | export, namespace |
| Coroutines (C++20) | co_await, co_return, co_yield |
| Operators (alt spellings) | and, and_eq, or, or_eq, not, not_eq, bitand, bitor, compl, xor, xor_eq |
| Miscellaneous | asm, auto, return, sizeof |
Note: The number of keywords C++ has evolved over time as new features were added to the language. For example, C++ 98 had 63 keywords, C++ 11 had 84 keywords, C++.
Keywords vs Identifiers
So, there are some properties of keywords that distinguish keywords from identifiers. They listed in the below table
| Keywords | Identifiers |
|---|---|
| Keywords are predefined/reserved words | identifiers are the values used to define different programming items like a variable, integers, structures, and unions. |
| It defines the type of entity. | It classifies the name of the entity. |
| A keyword contains only alphabetical characters, | an identifier can consist of alphabetical characters, digits, and underscores. |
| It should be lowercase. | It can be both upper and lowercase. |
| No special symbols or punctuations are used in keywords and identifiers. | No special symbols or punctuations are used in keywords and identifiers. The only underscore can be used in an identifier. |
| Example: int, char, while, do. | Example: geeksForGeeks, geeks_for_geeks, gfg, gfg12. |