Learn DSA in C++: Master Data Structure and Algorithm in C++

Data Structures and Algorithms (DSA) are fundamental parts of computer science that allow you to store, organize, and process data in ways that maximize performance. This tutorial will guide you through the important data structures and algorithms using C++ programming language.
Why Learn DSA in C++?
C++ is a powerful and high-performance programming language used for system/software development and game programming. Learning DSA in C++ instead of any other language have many advantages such as:
- Memory Management: Learning DSA in C++ gives you a deep knowledge of lower-level memory management which improves your understanding of data structures.
- Versatile: Knowledge of DSA in C++ is versatile and can be transferred to other languages, as many modern languages are built on similar syntax.
- Competitive Programming: C++ is widely used in competitive programming due to its speed and rich set of libraries allowing you to take an edge is problem-solving.
- Object Oriented: C++ allows you to implement data structures as classes, making your code closer to the real implementations of data structures.
Prerequisite
Before starting with DSA in C++, one should have a good knowledge of basic C++ concepts. The below is the list of fundamental concepts of C++ programming language which are the prerequisite for learning DSA in C++:
- Setting Up C++ Development Environment: For writing and running C++ source codes, your environment has to have a working C++ compiler and an IDE.
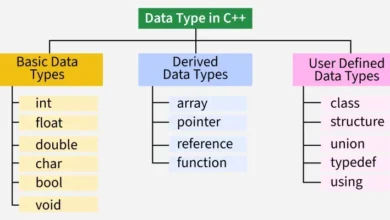
- Variables & Data Types: Variables are containers that store values, and each variable is associated with a specific data type, which defines the size and type of the data.
- Basic Input and Output: Input and output operations in C++ allows users to provide data to the program at runtime and print the data on the screen.
- Operators: Operators are used to perform many different operations on the C++ variables.
- Decision Making Statements: Decision making statements are used to include the conditional code in the program that will be executed if the given condition is true.
- Loops: Loops are used to repeat a block of code multiple times without writing it again and again in the source code.
- Function: Functions are the block of statements enclosed inside {}. They provide modularity and reusability in the program.
- User-Defined Data Types: We can define our own custom data type in C++ according to our needs. These custom data types are called user defined data types.
- Standard Template Library (STL): C++ STL provides a built-in implementation of commonly used data structures and algorithms. You can use STL in problem solving, but it is recommended to avoid using it while learning data structures and algorithms.
Learn DSA in C++
Mastering DSA in C++ will improve your problem-solving abilities and also prepare you for technical interviews, competitive programming, and real-world software development. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced, this guide is designed to provide you with a strong foundation in one of the most important areas of computer science.
Asymptotic Analysis of Algorithms
Asymptotic analysis of algorithms is a method used to evaluate the performance and efficiency of an algorithm. It evaluates how the execution time or memory requirements of an algorithm grow as the input size increases.
- Asymptotic Analysis of Algorithm
- Asymptotic Notation
- Best, Average and Worst Cases
- Analysis of Loops
- Analysis of Recursion
Bit Manipulation
Bit manipulation involves performing operations directly on binary digits (bits) to optimize different operations.
- Extract bits
- Setting bits
- Clearing bits
- Toggling bits
- Counting Set bits
Arrays
An array is a data structure that holds a fixed size collection of elements of the same type in continuous memory. These elements are accessed by their position or index.
- Arrays in C++
- 1D Array
- Multidimensional Arrays
Matrix
2D array are used to represent the concept of matrix in C++. It is arranged in the form of rows and columns.
- Transpose of Matrix
- Matrix Addition
- Matrix Multiplication
- Matrix Rotation
Strings
Strings are used to represent textual data. They are the sequence of characters terminated by a ‘\0’ NULL character.
- Strings in C++
- Reverse a String
- String Concatenation
- String Tokenizing
Pointers & References
Pointers and references in C++ are the variables that refer to another variable in the memory.
- Pointers
- References
- Pointer to an Array
Dynamic Memory Allocation
In C++, dynamic memory allocation allows the array and other data types to change their size in program’s runtime.
- new and delete Operators
- What is Memory Leak?
Linked List
A linked list data structure is a sequence of elements called nodes connected using pointers. Each node contains a value and a pointer to the next node in the sequence.
- Linked List in C++
- Singly Linked List
- Doubly Linked List
- Circular Linked List
Stacks
A stack is a linear data structure that follows the Last-In-First-Out (LIFO) principle where elements are added and removed from the top (from one side). Stacks are not implemented independently, instead they are implemented over other data structure.
- Stack in C++
- Stack Implementation Using Arrays
- Stack Implementation Using Linked List
Queues
A queue is a linear data structure that follows the First-In-First-Out(FIFO) principle where elements are added at the rear (one end) and removed from the front (other end). Just like stacks, queues are also implemented over other data structures.
- Queue in C++
- Queue Implementation Using Arrays
- Queue Implementation Using Linked Lists
- Circular Queue
- Double-Ended Queue (Deque)
Divide and Conquer Algorithms
Divide and Conquer algorithms divides a problem into smaller subproblems, solves each subproblem independently, and then combines their solutions to provide the final solution of the original problem. These algorithms depend mainly on recursion.
Following are some standard Divide and Conquer algorithms:
- Tower of Hanoi
- Convex Hull
- Closest Pair of Points
- Karatsuba Algorithm for Fast Multiplication
- Strassen’s Algorithm for Matrix Multiplication
Backtracking Algorithms
Backtracking algorithms solve problems by exploring all possible solutions and backtracking when a solution path fails to meet the problem’s conditions.
Following are some standard backtracking algorithms:
- Knight’s Tour Problem
- Rat in a Maze
- N-Queen Problem
- Sudoku
Searching Algorithms
Searching algorithms are used to find a particular element in a data structure like linked list, arrays, etc.
- Linear Search
- Sentinel Linear Search
- Binary Search
- Ternary Search
Sorting Algorithms
Sorting algorithms provides efficient ways to arrange the given data structure in desired order.
- Selection Sort
- Bubble Sort
- Insertion Sort
- Merge Sort
- Quick Sort
- Iterative Quick Sort
- Heap Sort
- Radix Sort
- Counting Sort
- Bucket Sort
Hashing
Hashing is a technique used to map data of any size to fixed-size values, known as hash codes. It is widely used in for fast data retrieval, encryption, and implementing efficient data structures like hash tables.
- Direct Address Tables
- Hashing Functions
- Hash Tables
- Collision Resolving
- Separate Chaining
- Open Addressing
Tree
A tree is a hierarchical data structure consisting of nodes where each node contains a data field and references (or pointers) to its child nodes. A tree in C is represented by a pointer to the root node (topmost node in the tree).
- Binary Tree
- Tree Traversal
- BFS Tree Traversal
- DFS Tree Traversal
- Binary Search Tree (BST)
- Self-Balancing BST
- AVL Tree
- Red-Black Tree
- B-Tree
- B+ Tree
- Advanced Tree Data Structures
- Segment Tree
- Trie (Prefix Tree)
- K-D Tree
Heap
A heap is a specialized tree-based data structure that satisfies the heap property: In a max-heap, each parent node is greater than or equal to its child nodes. In a min-heap, each parent node is less than or equal to its child nodes.
- Binary Heap
- Min Heap
- Max Heap
- Priority Queue
- Binomial Heap
- Fibonacci Heap
Graph
Graph is a data structure that is made up of nodes (also called vertices) connected to each other using edges. Graphs are commonly used in networking, social networks, and various algorithms like pathfinding and traversal.
- Graph in C++
- Classification of Graphs
- Directed Graph
- Undirected Graph
- Weighted Graph
- Unweighted Graph
- Graph Representation
- Adjacency Matrix
- Adjacency List
- Graph Traversal
- Breadth First Search (BFS) Traversal
- Depth-First Search (DFS) Traversal
- Graph Cycle Detection
- Minimum Spanning Trees
- Prim’s Algorithm
- Kruskal’s Algorithm
- Shortest Path Algorithms
- Dijkstra’s Algorithm
- Floyd-Warshall Algorithm
- Bellman-Ford Algorithm
- Johnson Algorithm
- Strongly Connected Components (SCC)
- Kosaraju’s Algorithm
- Tarjan’s Algorithm
- Topological Sorting of Graphs
- DFS-based Topological Sorting
- Kahn’s Algorithm
Greedy Algorithms
Greedy algorithms are a class of algorithms that make the choices by selecting the best available option at each step (i.e. local optimum) in the hope that it will lead to a global optimum solution.
Following are some standard Greedy algorithms with their implementation:
- Fractional Knapsack
- Activity Selection Problem
- Job Sequencing Problem
- Huffman Coding
Dynamic Programming Algorithms
Dynamic Programming algorithms involve solving the problems by breaking them down into smaller overlapping subproblems and storing the solutions to these subproblems to avoid repeated calculations.
Following are some standard Dynamic Programming algorithms:
- Rod Cutting Problem
- Coin Change Problem
- Edit Distance
- 0-1 Knapsack
- Longest Increasing Subsequence
- Partition Equal Subset Sum
- Subset Sum Problem
- Maximum Subarray Sum
- Minimum Cost Path
- Maximum Product Subarray
- Longest Common Subsequence
- Longest Palindromic Subsequence
Pattern Searching Algorithms
String algorithms deal with the manipulation and processing of sequences of characters. Common tasks include searching, matching patterns, and modifying strings.
- Rabin Karp
- Knuth-Morris-Pratt
- Boyer-Moore
Data Structures and Algorithms Complete Course using C++ – We’ve got a course for you – DSA Self-Paced which can help you to upskill yourself, be able to solve competitive programming questions, and get you placement-ready. No matter whether you’ve complete knowledge of DSA or not, no matter whether you’re a beginner at DSA, these factors can never be a hurdle if you’re someone who really wants to upskill and build a career in DSA.
What’s next?
Now that you have a strong foundation in DSA with C++, you can explore more advanced topics such as advanced graph algorithms and design patterns. Keep challenging yourself with complex problems, contribute to open-source projects, or even start preparing for competitive programming contests. Your journey in mastering DSA has just begun!