Standard Template Library (STL) in C++
STL is a collection of pre-built classes and functions that make it easy to manage data using common data structures like vectors, stacks, and maps. It saves time and effort by providing ready-to-use, efficient algorithms and containers.
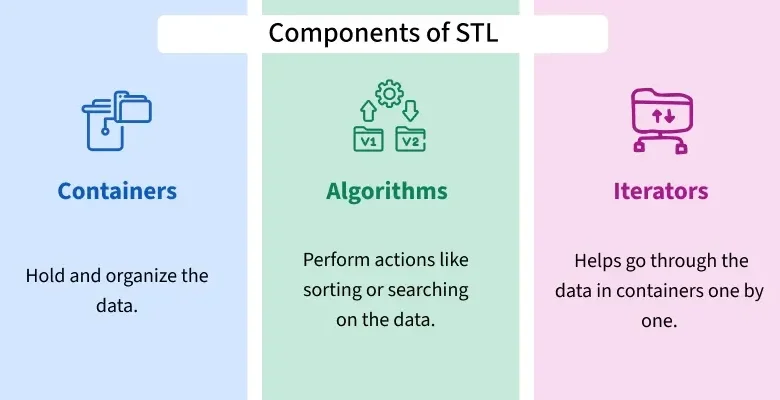
Components of STL
The components of STL are the features provided by STL in C++ that can be classified into 3 types:

These components are designed to be efficient, flexible, and reusable, making them an integral part of modern C++ programming.
Containers
Containers are the data structures used to store objects and data according to the requirement. Each container is implemented as a template class that also contains the methods to perform basic operations on it. Every STL container is defined inside its own header file.
Containers can be further classified into 4 types:
- Sequence Containers : Vector, Deque, List, Forward List, Array
- Container Adaptors : Stack, Queue, Priority Queue
- Associative Containers : Set, Multiset, Map, Multimap
- Unordered Associated Containers : Unordered Set, Unordered Multiset, Unordered Map, Unordered Multimap
Instead of writing your own data structures (like linked lists or stacks), STL provides ready-made containers that are: Fast, Reliable, Easy-to use and Type-Safe (work with any data type using templates).
Algorithms
STL algorithms offer a wide range of functions to perform common operations on data (mainly containers). These functions implement the most efficient version of the algorithm for tasks such as sorting, searching, modifying and manipulating data in containers, etc. All STL algorithms are defined inside the <algorithm> and <numeric> header file. Some of the most frequently used algorithms are:
- Sort : Arranges elements in ascending order (default).
- Binary Search : Checks whether a value exists in a sorted range.
- Find : Searches for the first occurrence of a given value.
- Count : Counts how many times a value appears in the given range.
- Reverse : Reverses the order of elements in the given range.
- Accumulate : Computes the sum of all elements in the range.
- Unique : Removes consecutive duplicate elements.
- Lower bound : Returns iterator to the first element ≥ value in a sorted range.
- Upper bound : Returns iterator to the first element > value in a sorted range.
- Replace : Replaces all occurrences of old value with new value in the given range.
Iterators
Iterators are the pointer like objects that are used to point to the memory addresses of STL containers. They are one of the most important components that contributes the most in connecting the STL algorithms with the containers. Iterators are defined inside the <iterator> header file.
Benefits of C++ Standard Template Library (STL)
The key benefits of the STL is :
- Saves time and effort.
- Reliable and Tested
- Fast and Efficient
- Reusability
- Built-in Algorithms