Somos Sequence in C++ –
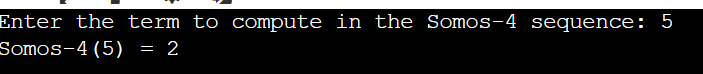
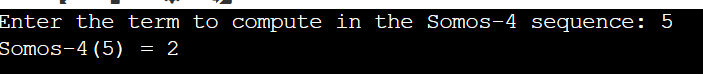
IntroductionThe Somos sequence is recursively defined in mathematics and is extremely interesting for its connections to elliptic curves, combinatorics, and algebraic geometry. The strange thing about this sequence is its propensity to result in integer values despite being defined by a fraction. The general form of a Somos sequence is given by: Sn=( sn-1sn-3+sn-2sn-2)/(sn-4) Where the initial conditions are carefully chosen positive integers. Understanding the Somos SequenceLet’s take an example of Somos-4, a well-known version of the sequence, which follows: Sn=( sn-1sn-3+sn-2sn-2)/(sn-4) With initial values: S1=S2=S3=S4=1 Calculating some terms manually: S5 = (1X1+12)/1=2 S6 = (1X2+12)/1= 3 S7 = (2X3+12)/1= 7 S8 = (3X7+12)/1= 23 It is quite surprising because all terms of this sequence are integers, while the recursive definition involves fractions. Recursive ApproachRecursive Implementation in C++There is a simple way to compute the Somos sequence: recursion. Let us take an example to illustrate the Somos Sequence in C++ using the Recursive Approach. Output:
Problems with Recursive Solution:
Optimized Solution: MemoizationWe use memoization (top-down dynamic programming) to store previously computed values to avoid recursion inefficiencies. Let us take an example to illustrate this approach. Output:
Benefits of Memoization:
Iterative Dynamic Programming ApproachInstead, we can eliminate this recursion and build an iterative variant (bottom-up dynamic programming approach), which is more efficient using both time complexity and space. Let us take an example to illustrate this approach. Output:
Advantages of the Iterative Approach
Further Optimization: Space Efficient ApproachWe only need the last four computed values, which allows us to use a rolling array approach to reduce space to O(1). Let us take an example to illustrate this approach. Output:
Final Complexity Analysis:
Conclusion:In conclusion, the Somos sequence is a strange construct from mathematics that is defined fractionally but remains integer-valued. We considered several approaches to computing it in C++. One was the naive recursive approach, and another was an optimized iterative version with a space complexity of O(1). This last version is the best implementation for actual use.
|