C++ if-else –
|
Programming languages rely on conditional statements to implement execution control through specific code blocks dependent on conditions. C++ programming offers the if-else statement because it is a fundamental conditional construct for making decisions. The if statement checks a provided condition to choose between running different sections of code based on truth or false. C++ includes multiple iterations of the if statement to manage different program requirements efficiently. In C++ programming, an if statement is used to test the condition. Types of if Statements in C++:There are various types of if statements in C++. Some of them are as follows:
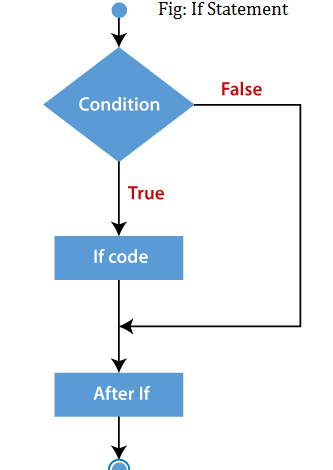
Each decision-making structure within C++ provides unique functionalities that boost programming flexibility because they perform distinct tasks. 1. C++ if Statement:The most basic form of conditional statement in C++ requires only an if statement. The C++ if statement tests the condition. It is executed if the condition is true. When the condition proves false, the program omits the subsequent if block. Syntax: It has the following syntax: Flowchart of if statement
C++ If Example: Let us take an example to illustrate the if statement in C++. ExampleCompile and Run Output: It is even number Explanation:
2. C++ If-else Statement:The C++ if-else statement also tests the condition. It executes if the block if condition is true otherwise else block is executed. Syntax: It has the following syntax: Flowchart of if-else statement
C++ If-else Example: Let us take an example to illustrate the if-else statement in C++. Output: It is odd number Explanation:
3. C++ if-else-if ladder Statement:The C++ if-else-if ladder statement executes one condition from multiple statements. Multiple cases can be handled through an if-else if conditional sequence in this structure. Syntax: It has the following syntax: Flowchart of if-else-if ladder statement
C++ if-else-if ladder Example: Let us take an example to illustrate the if-else-if ladder statement in C++. ExampleCompile and Run Output: Enter a number to check grade:66 C Grade Output: Enter a number to check grade:-2 wrong number Explanation:
4. Nested if Statement:The if statement structure includes another if statement within its body. Consecutive levels of conditional checks require the utilization of this statement. Syntax: It has the following syntax: Flowchart of nested if statement
Nested if Example: Let us take an example to illustrate the nested if statement in C++. ExampleCompile and Run Output: Enter your age: 18 Do you have an ID? (1 for Yes, 0 for No): 1 You are allowed to enter. Explanation:
Conclusion:In conclusion, C++ programs use if statements as basic decision tools, which trigger conditional responses based on different circumstances. Different variations consist of simple if alongside if-else, if-else-if ladder, and nested if along with the ternary operator to adapt to numerous conditions. A programmer’s selection of if statement type determines both the readability and efficiency as well as the maintainability of their code. Frequently Asked Questions:1. What role do C++ if statements serve in programming? C++ programming supports the if statement to enable decisions within programs. Program code blocks execute when a specified condition results in a true value through an if statement. When the expressed condition proves false, the following program block remains unexecuted. 2. What distinguishes if from if-else statements in the C++ language? The if statement runs its enclosed block when the specified condition proves true but does not run anything when the condition evaluates to false. The if-else statement grants two paths for program execution during conditional evaluation. The if statement runs its connected if block when the condition proves true or else the program moves to the else block. 3. How do consecutive if statements behave when there are no else conditions present in a C++ program? If statements are evaluated one by one when they appear without else condition. One or multiple code blocks can activate when multiple true conditions occur. 4. Explain the fundamental differences between an if-else-if ladder and a switch statement. An if-else-if ladder contains multiple conditional statements in a sequence that checks multiple conditions in C++. The condition evaluation stops after identifying the first true value in the chain. The switch statement becomes efficient for handling multiple cases through a single variable value when working with discrete values. 5. How do you define a nested if statement in C++? An if statement serves as an inner part of another if statement when it becomes a nested. The approach provides better decision opportunities because it verifies additional requirements once the initial external condition becomes true. Next TopicC++ switch
|